Audience
Central office divisions and Regional offices
Purpose
This procedure sets out the structured, systematic and timely approach for managing risk at an enterprise level across the Department of Education (the department).
Overview
Risk management refers to all of the actions taken to direct and control risk to achieve the department’s objectives. The department integrates risk management into all aspects of decision making and actions taken in day-to-day activities, as well as those that may impact on the department's strategic objectives.
This procedure defines the processes that enable enterprise, strategic and tactical risks to be identified, assessed (analysed, evaluated, treated), monitored and reviewed in a consistent manner, where they are assessed using the department’s enterprise risk management consequence and likelihood levels (DoE employees only).
Not all risks are assessed at the enterprise or strategic level. This includes risks arising from day-to-day activities in schools. Subject specific procedures (e.g., curriculum activity risk assessment procedure, and workplace health and safety related procedures) should be followed to manage these types of risks.
This procedure is to be read in conjunction with the department’s enterprise risk management framework and policy.
Responsibilities
All staff and contractors
- complete all mandatory risk training applicable to their role
- identify and report risks as part of day-to-day activities to a responsible officer or risk owner
- follow policies and procedures at all times to ensure compliance to minimise exposure to risks.
Additional responsibilities for staff with risk management roles (responsible officers)
- undertake activities to support the risk management process as directed by the risk owner
- record risks, monitor and maintain and update information in risk registers and action plans, including controls and actions
- escalate risks above acceptable risk tolerance level to risk owners.
Risk owners
- regularly review and assess risks for their business area
- endorse and oversee implementation and effectiveness of risk controls and actions
- endorse all assessed risk levels
- make decisions about how risks are to be managed.
Enterprise risk management key contact officers
- coordinate the risk reporting process for their business area (branch, division or region) to inform the department's quarterly risk review as administered by Governance, Strategy and Planning (GSP).
Control owner/action owners
- implement, monitor and maintain effective risk controls and actions
- provide advice and report to the risk owner on the effectiveness of controls and actions.
Strategic governance committees
- provide strategic oversight, monitoring and assurance of enterprise risks, strategic risks and tactical risks related to the committee's operation as provided in each strategic governance committees’ (DoE employees only) terms of reference
- monitor the performance and effectiveness of the department's internal controls
- promote the principles of risk management and champion a risk aware and responsive culture.
Audit and risk management committee
- provide independent audit and risk management advice to the department's Director-General to ensure good governance and accountable decision-making
- review and provide advice on the department's enterprise risk management framework and assurance processes.
Governance, Strategy and Planning
- coordinate the department's quarterly risk review and reporting process
- produce quarterly risk reports to support strategic governance committee monitoring and oversight
- administer the department's enterprise risk management (ERM) system.
Process
The department’s process to manage risk is based on the Australian Standard AS ISO 31000:2018 Risk management – guidelines:
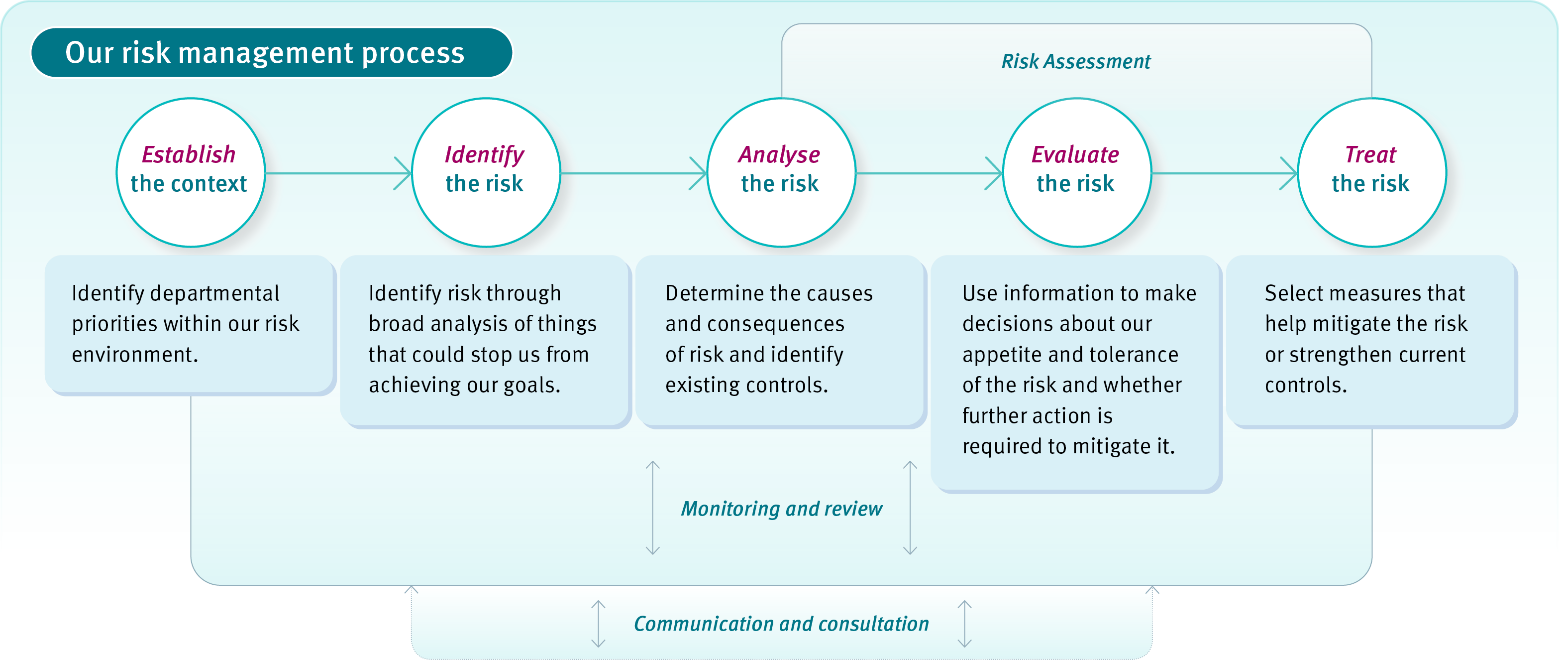
Image 1: Enterprise risk management flowchart
1. Establish the context
Understanding the context of the operating environment helps employees to identify relevant enterprise, strategic or tactical risks that may impact on the achievement of departmental, division/region or strategic objectives. To establish the risk environment employees must:
- review the department's risk appetite statement to understand how the department manages enterprise and strategic risks
- review strategic, operational and/or local area plans (plans), and have discussions about potential opportunities and threats with key stakeholders.
2. Identify the risk
Risk owners/responsible officers must identify risks that may impact on the achievement of priorities.
The risk owner/responsible officer must:
- conduct a comprehensive environmental scan to generate a list of potential challenges and opportunities. Risk owners/responsible officers may:
- use environmental analysis using tools such as SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats) and STEEPLE (social, technological, economic, environmental, political, legal and ethical)
- review strategic and operational plans and strategies
- benchmark against other organisations
- communicate and consult with internal and external stakeholders
- review past learnings, audits and assessments.
- document the risk event, and list all the possible causes and consequences of the risk. A generic risk assessment plan template (DoE employees only) can be used.
- determine the root cause of the risk by considering the possible causes and the key factors contributing to the particular risk event (this will assist when identifying potential controls to manage the risk)
- determine the most likely key impacts and possible consequences of the risk in achieving strategic objectives and priorities.
3. Analyse the risk
To determine the risk level, the responsible officer:
- must assess the likelihood and consequence of the risk using the enterprise risk consequence and likelihood tables and the department's risk matrix (DoE employees only)
- may assess the inherent risk level
- must document the controls that are able to effectively respond to the risk in the risk register
- must determine the current risk level by selecting the most appropriate consequence and likelihood level and record this in the risk register.
The risk owner must endorse the assessed current risk level and documented controls.
4. Evaluate the risk
To determine the risk appetite and target risk levels, the responsible officer must:
- determine the risk appetite level for the risk by deciding which risk category applies by referring to the department’s risk appetite statement, or
- set the risk appetite at low if the risk is aligned to an area of lowest risk appetite or the ‘legislation, regulation or compliance obligations’ risk category
- determine the target risk level (or the desired risk level) by considering the risk appetite and the acceptable risk tolerance level
- record the risk appetite and target risk level in the risk register.
The risk owner must endorse the assessed risk appetite and target risk level.
5. Treat the risk
If the current risk level is higher when compared to the target risk level the responsible officer/control owner/action owner must treat the risk by:
- deciding on appropriate actions and implementing them
- consulting with relevant stakeholders
- documenting actions in the action (treatment) plan. An example of an action plan is included in the enterprise risk assessment plan template (DoE employees only)
- escalating and reporting risks above target levels to the risk owner.
The risk owner must:
- endorse the actions to be implemented
- decide if risks above the target level are to be accepted, reassessed, or require further review of controls or actions.
6. Monitoring and review
The responsible officer/control owner/action owner must on a regular basis or at each risk review cycle:
- review/update the action (or treatment) plan
- provide advice and report to the risk owner on the effectiveness of controls and actions
- check that the risk is still relevant and applicable, and that the risk description accurately defines the causes and consequences of the risk
- check that the controls and actions being relied upon to manage and treat the risk are effective and working as intended
- reassess the current risk level
- communicate and consult relevant stakeholders
- escalate risks above the acceptable risk tolerance level to the risk owner.
The risk owner must on a regular basis or at each review cycle:
- endorse the controls and actions being relied upon to manage and treat the risk
- endorse the reassessed current risk level
- decide if risks above the acceptable tolerance level are to be accepted, reassessed, or require further review of controls or actions.
Escalate significant tactical risks for strategic oversight
The responsible officer must:
- assess whether the risk has a significant impact on the department's strategic priorities or an enterprise risk by using the department’s enterprise risk consequence and likelihood tables (DoE employees only)
- escalate a tactical risk to the strategic governance committee by updating the risk description to become a new strategic division/region risk e.g., where a project has multiple risks, a summarised overall strategic project risk description is required
- record the risk in the department’s enterprise risk management (ERM) system.
The risk owner must endorse the escalation of the risk through the division or region's local governance processes.
Reporting
All staff must report risks as part of day-to-day activities to a responsible officer or risk owner.
The risk owner must:
- establish regular reporting of risks through local governance processes to provide assurance that the risk is being managed and responded to appropriately
- report on enterprise and strategic objective risks to strategic governance committees on a quarterly reporting cycle, in line with the ERM quarterly risk reporting process (DoE employees only).
ERM key contact officers must:
- coordinate the risk reporting process for their business area (branch, division or region) each quarter to inform the department's quarterly risk review as administered by GSP
- ensure approved risk information is recorded and updated each quarter in the department’s ERM system.
Governance, Strategy and Planning must:
- coordinate the department's ERM quarterly risk reporting process (DoE employees only)
- produce quarterly risk reports to support strategic governance committee monitoring and oversight.
Definitions
|
Term
|
Definition
|
|
Action
|
A temporary, time bound measure introduced to reduce a risk to an acceptable level and/or improve an existing control.
|
|
Business unit risks
|
Risks that arise from the activities of a business unit and have an impact on business unit priorities.
Business unit risks are risks within the tactical risks group.
|
|
Consequence
|
The outcome of an event which affects the department’s ability to achieve its objectives.
|
|
Control
|
Any existing process, policy, device, system, practice or other method aimed at reducing the likelihood or consequence of a risk.
|
|
Current risk level
|
This is the level of risk with existing controls in place. The current risk level is reassessed at each review cycle after considering the impact of controls and actions.
|
|
Enterprise risks
|
Risks to the department’s areas of lowest appetite which are:
- child and student protection and safety
- workplace health and safety
- security of confidential and personal information (information security)
- our Integrity (fraud and corruption).
Enterprise risks are risks within the strategic objective risk group.
|
|
Enterprise risk management framework
|
The department’s approach and system of managing risk including policies, procedures, processes, and supporting information, and is represented through the enterprise risk management framework document.
|
|
Inherent risk level
|
The level of risk before any controls are applied.
|
|
Likelihood
|
The chance or probability of the risk consequence occurring as a result of the risk event.
|
|
Operational risks
|
Risks that arise from a division or region and have an impact on operational priorities.
Operational risks are risks within the tactical risk group.
|
|
Portfolio/program/project risks
|
Risks that arise from portfolio, program, or project activities.
Portfolio, program, project risks are grouped within the tactical risk group.
|
|
Risk
|
The chance of something happening that will impact the department’s ability to achieve its objectives. Risk is measured in terms of consequences and likelihood.
|
|
Risk appetite
|
Level of risk or opportunity the department is willing to accept in achieving its objectives.
|
|
Risk management
|
Coordinated activities to direct and control the department’s risks.
|
|
Risk owners
|
The Deputy Director-General, Assistant Director-General, Executive Director, or Regional Director who is accountable for the performance of strategic objective risks for their business area.
For tactical risks, risk owners may be a manager or above, or the Chair of a portfolio, program or project board.
|
|
Risk register
|
A tool used to record information about identified risks and how they are being managed. The department's enterprise risk management system is an online risk register used for recording, managing and reporting the department's strategic objective risks.
|
|
Risk tolerance
|
The variation from the established risk appetite which the department is prepared to accept.
|
|
Strategic division/region risks
|
Risks that have a significant impact on strategic delivery outcomes originating from a division or region’s operations.
Strategic division/region risks are risks within the strategic objective risk group.
|
|
Strategic objective risks
|
Enterprise, strategic, and strategic division/region risks.
|
|
Strategic risks
|
Risks to the achievement of the department’s strategic objectives as determined by the executive leadership team.
Strategic risks are risks within the strategic objective risk group.
|
|
Tactical risks
|
Operational, business unit and portfolio/program/project risks.
|
|
Target risk level
|
The desired acceptable risk level determined by considering the department's risk appetite and the acceptable risk tolerance level.
|
Legislation
Delegations/Authorisations
Other resources
Enterprise risk management tools
Related resources
Superseded versions
Previous seven years shown. Minor version updates not included.
7.0 Enterprise risk management